

- #RES2DINV TUTORIAL MANUAL#
- #RES2DINV TUTORIAL FULL#
- #RES2DINV TUTORIAL SOFTWARE#
- #RES2DINV TUTORIAL WINDOWS#
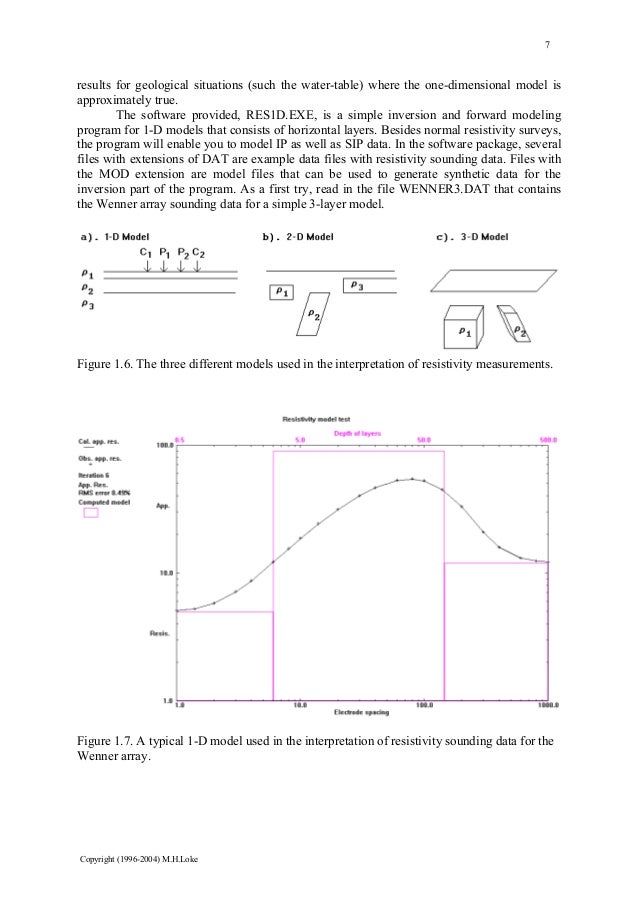
The three parameters are illustrated in Figure 7.1 for the dipole-dipole array as an example.įigure 7.1. The third parameter (only applicable to the pole-dipole, dipole-dipole and Wenner-Schlumberger arrays) is the ratio of the distance of the current electrode from the nearest potential electrode to the P1-P2 spacing. The second parameter is the spacing between the P1 and P2 potential electrodes (the ' a' spacing). The first parameter is the location of the first (leftmost) electrode or the mid-point of the array. The index based data format use a maximum of three parameters to specify an array. Standard Conventional Arrays (Wenner, Wenner-Schlumberger, Pole-Pole, Dipole-Dipole)Īny array with regular spacing, that can be described by only 3 parameters, is considered standard and data file uses “ index based data format”. Gradient array (only used as sub-array number with data in the general array format) Offset pole-dipole (only used as sub-array number with data in the general array format)Ĭross-borehole survey (apparent resistivity values)Ĭross-borehole survey (resistance values) The RES2DINV program will automatically convert a Wenner beta array data file into a dipole-dipole array data set.Ī list of the arrays supported by the RES2DINV program together with their number codes are given below. The Wenner beta array is a special case of the dipole-dipole array where the "n" factor is always 1. The "normal" Wenner array is actually the Wenner alpha array. The Wenner array has three different variations (Figure A.1). In general for an array with four electrodes, there are three possible arrangements for the electrodes. Table A.1 shows the arrangement of the electrodes, names and codes for some commonly used arrays.
#RES2DINV TUTORIAL FULL#
Therefore, the Table and Figure numbering was kept constant with originals, which can be downloaded as full PDFs from the attachment to this blog post.Ī description of the different arrays types is given in the free tutorial notes on electrical imaging (Loke, 2011).
#RES2DINV TUTORIAL MANUAL#
Information below is compiled from RES2DINV Manual and Loke’s Course Notes to facilitate data file preparation and usage in RES2DINV for beginners. The general array format can be used for any array, including gradient and non-conventional arrays of any configuration.
The older index based format is only used for conventional arrays such as the Wenner, Wenner-Schlumberger, pole-pole, pole-dipole and dipole-dipole arrays. There are two main types of data format used by RES2DINV, an index based and a general array format.

If there is a problem in running RES2DINV software, one possible cause is that the input data were arranged in a wrong format. The data are arranged in an ASCII delimited manner where a comma or blank space or LF/CR is used to separate different numerical data items.
#RES2DINV TUTORIAL WINDOWS#
Some tips on using Windows Notepad for simple text file editing can be found here. You can use any general purpose text editor, such as the Windows Notepad program if you are creating the data file manually.
#RES2DINV TUTORIAL SOFTWARE#
The apparent resistivity values (and IP) used by RES2DINV software are given in a text file with. Besides normal surveys carried out with the electrodes on the ground surface, the program also supports aquatic and cross-borehole surveys.
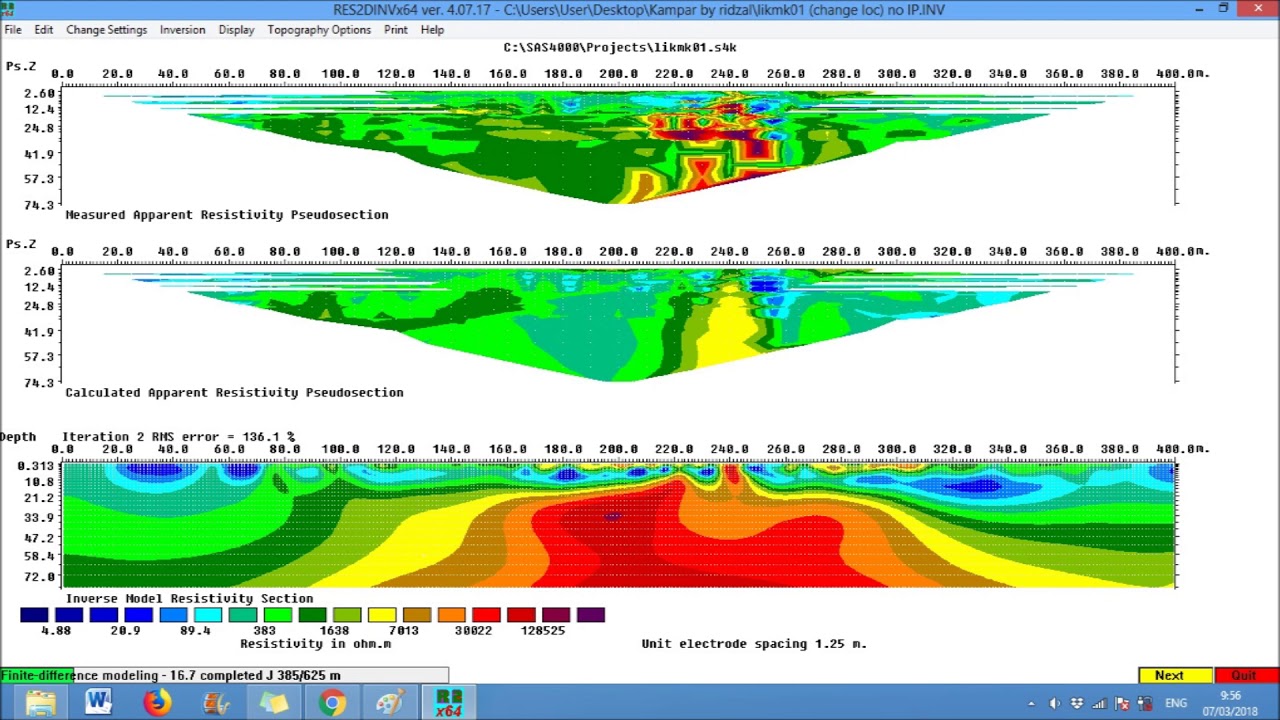
You can process pseudo sections with up to 16000 electrode positions and 70000 data points at a single time on a computer with 4 gigabytes (GB) of RAM. In addition to these common arrays, the program even supports non-conventional arrays with an almost unlimited number of possible electrode configurations (Loke et al. RES2DINV program can be used for surveys using the Wenner, pole-pole, dipole-dipole, pole-dipole, Wenner-Schlumberger, gradient and equatorial dipole-dipole (rectangular) arrays. However, the program can also handle data sets with a non-uniform electrode spacing. The survey is usually carried out with a system where the electrodes are arranged along a line with a constant spacing between adjacent electrodes. This program is designed to invert large data sets (with about 200 to 100000 data points) collected with a system with a large number of electrodes (about 25 to 16000 electrodes). Many different multi-electrode systems have been developed over the past 15 years using different arrangements of the cables and measurement strategies (Loke, 2011). Formatting Array Input Data File in RES2DINV: surface electrodes for any geometryĮxample of electrodes arrangement and measurement sequence that can be used for a 2-D electrical imaging survey is shown on the left.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
